Blending Bio Inspired Algorithm and Cross Layering for Optimal Route in MANETS; 6G Scenario
Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, Volume 4, Issue 9, Page # 22-29, 2025; DOI: 10.55708/js0409003
Keywords: MANET, Routing, PSO, ACO, Cross Layer, MAC
(This article belongs to the Section Interdisciplinary Applications – Computer Science (IAC))
Export Citations
Cite
Inamdar, S. R. and Kallibaddi, J. I. (2025). Blending Bio Inspired Algorithm and Cross Layering for Optimal Route in MANETS; 6G Scenario. Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, 4(9), 22–29. https://doi.org/10.55708/js0409003
Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar and Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi. "Blending Bio Inspired Algorithm and Cross Layering for Optimal Route in MANETS; 6G Scenario." Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences 4, no. 9 (September 2025): 22–29. https://doi.org/10.55708/js0409003
S.R. Inamdar and J.I. Kallibaddi, "Blending Bio Inspired Algorithm and Cross Layering for Optimal Route in MANETS; 6G Scenario," Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 22–29, Sep. 2025, doi: 10.55708/js0409003.
In order to find the best path in 6G scenario, this paper suggests a directional routing approach for Mobile Ad hoc NETworks (MANETs) that investigates clubbing of updated Tunicate Swarm Algorithm (TSA), an updated intensification technique inspired by biology and Cross Layer Interaction (CLI). To address its previous shortcoming of trapping into local optima, updated TSA, which replicates the jet impulse and swarm actions of tunicates, has been modified. Through the use of CLI, the network density parameter is transferred between layers. In the the medium access protocol of directional antenna enabled MANETs, it is suggested that the directional monitoring time, optional handshake, and data fragment length be changed to lessen load on the routing protocol. Simulation results demonstrate that, when compared to competing proposals, Bio inspired algorithm and Cross layering blending-based routing approaches in MANETs yield better results.
1. Introduction
An ad hoc network is a kind of wireless network that is portable, allows for unrestricted mobility, and links devices of the same status on the network. In addition to functioning as relays and being in charge of effectively managing and structuring the network, the nodes are permitted to chain neighboring nodes as long as they are within their range. Numerous vision-based applications across numerous industries have been spawned by the advantages of ad hoc networks, including their mobility, adjustability, robustness, and in-coherence. Based on their intended use, wireless ad hoc networks are divided into three clubs: Vehicular Ad hoc NETworks (VANETs), which uses operating vehicles to build a network; Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), which uses separate sensors to control environmental parameters; and Mobile Ad-hoc NETworks (MANETs), which primarily consists of personal digital assistances [1].
This probe improves non-linear artificial problems using a modified Tunicate Swarm Algorithm (TSA), a metahiuristic algorithm that takes inspiration from nature. The swarm behavior of tunicates, which live in the deep ocean, served as the model. TSA provides an incentive to find solutions for MANET concerns. The following are some of the exceptional social nature of MANETs that can be effectively resolved by employing a metaheuristic approach. The existence of multiple node linking options, the establishment of node collaboration, A backup method for broken links, the self-association nature of the network and Spontaneous and healthy variation to address topology and traffic disturbances.
This probe has the following noteworthy additions:
- Network Density (ND) is measured from the network layer.
- Stable routes are established through enhanced bio-inspired TSA.
- To ensure flexibility or adaptation, Cross Layer Interaction (CLI) is used to pass the Network Density (ND) parameter.
As described below, this paper is standardized as follows. In the second section, we introduce basics of directional communication, CLI, other bio-inspired algorithms and TSA. Directional Monitoring concept used in Directional Medium Access Control (DMAC) and method to calculate ND are also summed in second section. Third section advocates the proposed routing protocol approach. The last section describes the simulation environment and highlights results followed by conclusion and possible future work.
2. Directional Communication, Concepts of Cross Layering, Bio-inspired algorithm and Adaptive Directional Monitoring
For the communication between nodes on a MANET, the Medium Access Control (MAC) layer of the MANETs previously preferred omni-directional antennas due to cost constraints and relies on a best-effort approach for the delivery of data packets. However, when Smart Antenna (SA) technology providing directional transmit or communication is used in MANETs in contrast to the traditional omni-directional antennas, the use of wireless media is greatly improved at the expense of problems such as directional hidden terminals caused by the lack of information on the channel status during antenna orientation of the node. An appropriate, agile MAC protocol is necessary to exploit the advantages of directional antenna.
Once DATA-frame fragmentations and short busy advertisement signals are able to communicate the communication situation to the directional hidden nodes of MANETs, the MAC protocol for MANETs with agile directional antennas will be able to overcome the directional hidden-node problem. By choosing the right fragment number and adaptively adjusting the data-fragment length, it can therefore decrease the frame collisions caused by the directional hidden nodes and boost the network throughput in comparison to the traditional protocol. To address the hidden terminal issues, directional beams are sent with the data fragments and Acknowledgments (ACK) to be sent. This allows for directional node monitoring. There won’t be a directional hidden node issue because directional monitoring allows every node to be aware of the receiver condition during the Directional Monitoring Period (DMP). Additionally, the DMP period can be adjusted to improve the routing protocol’s overall performance.
Layered design is assumed by a significant portion of the suggested routing protocols in MANETs. Because each layer-specific protocol designs only takes into account interaction with its neighboring layers, this design approach is extremely rigid and non-adaptive. Setting up meaningful interactions between different layers using the Cross Layering approach is important in recent protocol design approaches for MANETs in order to improve performance. Cross layer interaction between the physical, MAC, and routing layers is commonly used in cross-layering-based new protocols for MANETs in order to reduce protocol overhead and prevent collisions during data transmission. When social water particles are used to find and maintain high connectivity paths in unstable MANETs, routing protocols with lower end-to-end delay and route discovery latency are created. Concept of collective behavior in the updated Tunicate algorithm, where each person acts independently but nevertheless produces intended output.
In MANETs, CLI and biological process-based routing protocols show promise as against traditional methods for determining the globally optimal path. Theoretically and practically substitutes, these routes are also found to be Quality of Service (QoS) aware and fault tolerant [2]. The detailed abbreviations and definitions used in the paper are listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Abbreviations and their definitions
Acronym | Definition | Acronym | Definition |
ACO | Ant Colony Optimization | CLI | Cross Layer Interaction |
CBR | Constant Bit Rate | DMAC | Directional Medium Access Control |
DMP | Directional Monitoring Period | MAC | Medium Access Control |
MANETs | Mobile Ad-hoc NETworks | ND | Network Density |
PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization | SA | Smart Antenna |
QoS | Quality of Service | TCDMAC | TSA and CLI enabled Directional MAC Protocol |
TCDRP | TSA and CLI enabled Directional Routing Protocol | VANETs | Vehicular Ad hoc NETworks |
TSA | Tunicate Swarm Algorithm | WSNs | Wireless Sensor Networks |
2.1. Cross Layering
In many MANET applications, the CLI design approach which emphasizes communication between multiple layers has proven to be a workable solution. It enables dynamic adaptation and fine tuning of protocol constraints during the blueprint phase, ideally allocating important data during run-time. The benefits of a CLI enabled MANET include planning conventions that adapt network conditions and supporting applications with constant, universal access to resources and control requirements. Dynamic network structure brought on by node movement raises the possibility of severing a connection with a neighbor, but neighbor, but it also raises the possibility of finding a quicker route to the target node in the event of group mobility [3]. In order to create adaptive protocols, the status of network’s current information will now be stored in the network stack across various layers. Data streams between different layers of the protocol stack are needed for connections between them. The CLI approach in MANETs is motivated by [4]:
- Protocol overhead, security, topology control, and QoS are among the issues in MANETs that require the active participation of multiple layers.
- MANETs can be used for more applications if multiple protocol stack layers are aware of the channel status, congestion level and traffic density.
- The protocols ought to be flexible and adaptable to the needs of MANET applications.
- Adjusting the protocol’s parameters in proportion to the current network state improves the network protocol’s agile property.
2.2. Bio-inspired algorithms
Swarm intelligence, which comes from a computational intelligence approach, is used to solve a number of complex optimization problems. Researchers are especially fond of algorithms that draw inspiration from biology and recommend few parameter changes in these algorithms. Two well-liked algorithms in this field for global optimization problems are Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [5]. These algorithms are made to mimic the collective behavior of ant colony and fish schools or flocks of birds, where each particle roams around a designated search area and updates its current state in relation to the global value until a satisfactory solution is found [6]. The behavior of MANETs, which results from the redundant local collaboration of individual specialists with peers as well as their environmental factors, has been extensively studied using population-based methods or techniques such as ACO and PSO.
When artificial ants in ACO mimic the foraging behavior of real ants, complex combinatorial streamlining problems are resolved to a higher fulfillment level. During their search, real ants leave pheromones on the ground, and these pheromones cause abnormal correspondences between ants. Pheromone path update and pheromone path vanishing rate are the administrators used in ACO. By accurately simulating the scrounging behavior, MANETs plan the computations using these administrators and the ACO control boundaries.
If ACO ant agents are used, routing in MANETs is designed with a lower end-to-end delay and a lower route discovery delay. If ACO-based algorithms are used in routing, energy awareness, route discovery, and maintenance of high connectivity paths are developed, which extends the MANETs lifespan. Additionally, MANET routing protocols based on the ACO algorithm can achieve higher performance at low routing overhead with fluctuating node counts, data volumes, and node movement.
AntNet [7], Hybrid ACO [8], AntHocNet [9], ACO-enabled routing in MANETs [10], On-demand distance vector ACO algorithm [11], ACO-based routing [12], ACO with QoS [13-14], a new version of the self-organized algorithm (EARA) [15], Enhanced with QoS [16], BeeAdHoc [17], an energy-efficient routing protocol, and energy-aware AOMDV (EA-AOMDV) [18] are a few examples of bio-inspired routing protocols that have been documented in the literature.
The social interaction of water particles is the focus of the efficiency adaptation technique known as PSO. Using this method, the initial number of particles is distributed throughout the solution space S. Each particle in S moves at a different speed. The gross population and each fragment (specific ideal) converge at the best price (overall ideal). After each cycle, the fragment modifies its level in accordance with the overall and specific ideal ratings.
There is always the question of whether more optimization algorithms are needed given the vast array of optimization techniques available. Its solution is the No Free Lunch (NFL) theorem, which states that due to the complexity and unique nature of each problem, a single intensification technique is insufficient for all of them [19]. Researchers are motivated by the NFL hypothesis to develop novel optimization strategies that can tackle a variety of problems.
2.2.1. Bio- Tunicate Swarm Intelligence
Tunicates are able to locate food sources within the ocean. The optimal food source is chosen in this work based on two tunicate traits. Two examples of these characteristics are jet momentum and swarm intellect. To mathematically express jet propulsion habits, tunicates must meet three requirements; avoid collisions with other search agents, move in the direction of the ideal location, and remain near the ideal search agents. Other search agents will stay informed about the best possible solution thanks to the swarm nature.
The ideal initial solutions will be replicated and other search agent’s positions will be improved to match the ideal search agents’ locations in order to mathematically simulate tunicate’s swarm actions. The swarm intellect of tunicate is interpreted using the formula below.
$$P_p(\vec{x}+1)=\frac{\vec{P}_p(x)+P_p(\vec{x}+1)}{2+C_1}\tag{1}$$
where variable , is random number and the vector represents the location of tunicate.
The proposed modified TSA algorithm is as follows and flowchart is depicted as in figure 1.
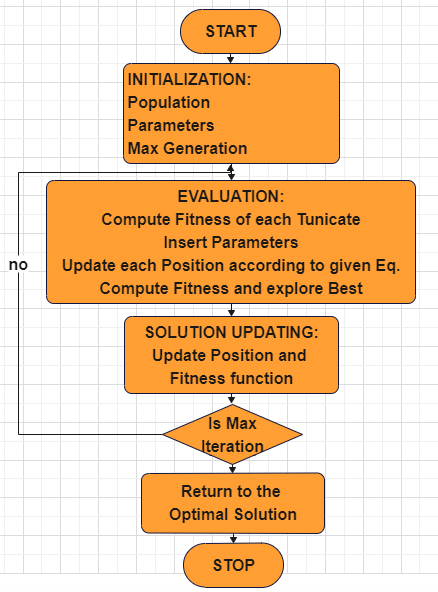
Algorithm 1: Modified TSA algorithm |
Result: Optimal route |
Step 1: Phase of Pre-requisite: The crowd of tunicates in a particular search area is started at random. Additionally, the algorithm’s initial values, population size, and generation threshold limit (t) are assigned. Step 2: Phase of Estimation: According to the specified fitness function, each tunicate is estimated. Step 3: Phase of Refinement: Every location in the search formula relates to an active step; if it yields better results than the previous one, it is ideal. In this case, the searching space’s limiting boundaries are dynamically altered. Step 4: Phase of Re-condition: Eq. (1) is used to update the tunicate crowd. To carry out the exploration capability, every area of the search space is taken into consideration. To fine tune the optimal solution, the fitness function of each tunicate is computed. Step 5: Iterations: Second step to fourth step repeated till the condition of termination is reached. |
The maximum area of the search region is taken into account when executing exploration ability using (1). The suggested algorithm can increase exploitation capability by taking advantage of missing regions using (2) [20]. In order to prevent local optima trapping, a balance between exploration and exploitation is thus achieved.
$$P_{\text{pop}}(t+1)=P_{\text{pop}}(t)\pm \mathrm{rand}^t \times (\alpha \mid 2)\tag{2}$$
where α is a dynamic step that shrinks as the optimization process continues to focus local searching.
2.3. Adaptive Directional Monitoring
The well-known hidden node problem is avoided by the method of directionally checking the receiver’s condition prior to data transmission from the sender node [21]. The directional hidden terminal issue is largely resolved when DMP is integrated into the medium access strategy. RTS/CTS transmission followed by DATA/ACK transmission is the process used in DMP-enabled MAC to to establish mutual consent between source and destination. However, some problems still occur when using the MAC approach with a fixed DMP value. While hidden terminal issues cannot be prevented for smaller or marginal DMP values, the protocol incurs additional overhead for very large DMP values. As a result, DMP becomes adaptive; its value corresponds to the size of the packets that need to be sent. The initial value for DMP is decided after a number of test flows in different types of topologies are completed.
Therefore, adaptation of DMP value is as follows:
- For transmission of shorter routing packet at Sender node, DMP will be decreased using λ, Now: New DMP = DMP – λ
- For transmission of longer routing packet at Sender node, DMP will be enhanced using δ, Now: New DMP= DMP+ δ
2.4. Calculating Network Density
To determine the calculation of ND, solutions to network problems utilizing physics concepts are examined. To compute the ND, the following equation is suggested [22];
$$\mu=\frac{N\pi R^2}{A}\tag{3}$$
In this case, N stands for the number of nodes in locality A, and R. represents the transmission range. A more accurate formula defines the ND as follows [23];
$$d(r)=\lim_{|A|\to 0}\frac{N(A)}{|A|}\tag{4}$$
Here: Nodes per m2 is the unit to describe node density.
The ND calculation makes the assumption that it is a particular quantity that is limited to a certain area and depends on the transmission range. Other factors (like mobility, obstacles, etc.) are not included in the ND calculation and could affect the calculation of connected nodes.
3. Proposed Routing and Medium Access Approaches
Flexible planning rules that adjust to shifting network conditions and give applications reliable control over important resources and their administration are advantageous to CLI-enabled MANETs. The proposed method is based on a modified searching technique that replicates jet impulse and swarm conduct in order to improve TSA’s exploration and exploitation issues.
A new directional routing technique, the Tunicate swarm algorithm and Cross layer integration enabled Directional Routing Protocol (TCDRP), is proposed with the help of enabling 6G technologies. To determine its benefits, TCDRP is contrasted with benchmark and the most recent directional routing approach-based protocols. TCDRP is designed to take full advantage of blending updated Tunicate swarm algorithm and Cross layer interaction enabled Directional Medium Access Protocol [TCDMAC]. Figure 2 displays a block diagram of the TSA and Cross layering-based routing approach.
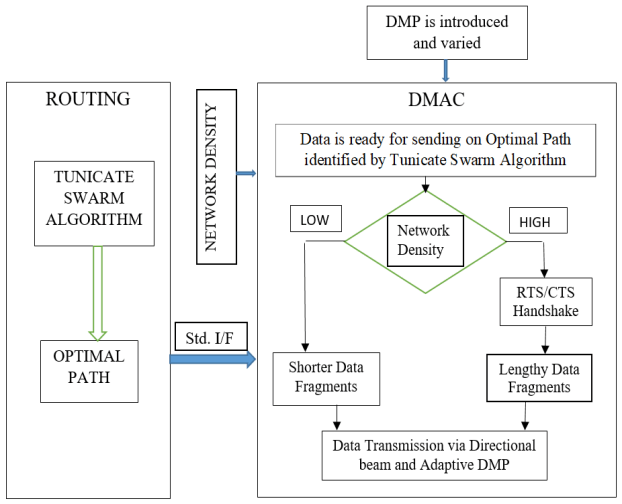
Actions taken in TC and TCDRP are as below:
3.1. Steps in TCDRP Approach
Step 1 Examine every possible route from the sender to the destination in the input set.
Step 2. As tunicate particles, chart these identified paths.
Step 3. Modified TSA is used to determine the best route.
Step 4. The source node sends the desired data to target node via the TCDMAC protocol using the nodes found on the optimal path.
3.2. Steps in TCDMAC Approach
Step 1. TCDRP first determines which path offers the best route for data transmission.
Step 2. To determine the network’s condition, estimate the parameter ND.
Step 3. Verify that the value of ND has reached its threshold
Once the data is ready to be sent;
if (YES) send data with RTS/CTS handshake; Send lengthy data fragments
else send data without RTS/CTS handshake; Send shorter data fragments ( to reduce overhead)
Step 4. Data packets are converted into data fragments. The length of the data fragment is proportional to the estimated ND. Use IFDS to transmit continuously.
Step 5. Directional antennas are used to transmit data fragments.
Step 6. It makes use of adaptive DMP.
Step 7. Retransmit the data if there is transmission error.
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
Network Simulator (NS2) is recommended to validate the suggested method [24]. Nodes are permitted to move within a designated simulation area of 1.3 kilo sq m for a time period of 50 seconds. Each node with simulation traffic of Constant Bit Rate (CBR) has a 250-meter transmission capability. Table 2 shows the specifics of the simulation environment along with a few important parameters. Iterative simulations are conducted, and performance matrices are plotted using average values.
Table 2: Specifications of the simulation environment.
Nodes in simulation setup | In steps of 20 from 20 to 100 |
Applied simulation area | 1.300 X 1.300 square KMs |
Medium Access protocol | IEEE 802.11 |
Transmission distance | 250m |
Time period of simulation | 50 sec |
Origin of Traffic | CBR |
Identified size of packet | 512 |
Packet transfer rate | In steps of 50 (50 to250kbps) |
Architectures of Network | Non-Linear |
Propagation scheme | Two Ray Ground |
Antenna mode | Omni/Dir Antenna |
Count of directions | 4 |
Modulation | BPSK |
4.1. Performance Metrics
To judge the total performance gain, the suggested TCDRP approach is contrasted with the fundamental directional routing approach DRP [25]. In order to observe improvements over the most recent routing protocol, CEELBRP, non-linear network topology is used, which varies the number of nodes and traffic rates as well as execution metrics [26]. The following metrics are considered in the suggested method’s performance.
The number of packets that did not reach their intended destination during their journey from source to destination nodes is indicated by the packet delivery ratio. It is computed by dividing the number of packets sent by the sender by the number of packets received at the recipient.
- Packet Drop: Described in terms of average packet drops, this is a sign of either poor service or erratic network connectivity.
- Throughput: Throughput is the rate at which information is sent over the network being tested.
- Delay: This summative term takes into account four distinct elements and measures how long it takes for nodes to send the allocated data packets.
4.2. Based on number of nodes
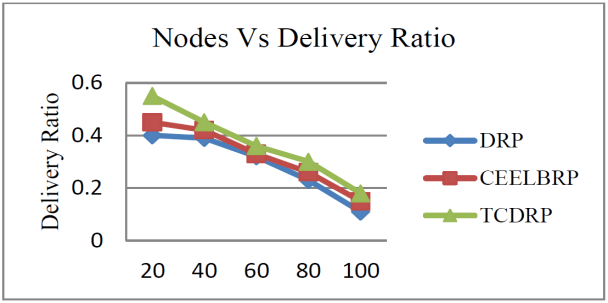
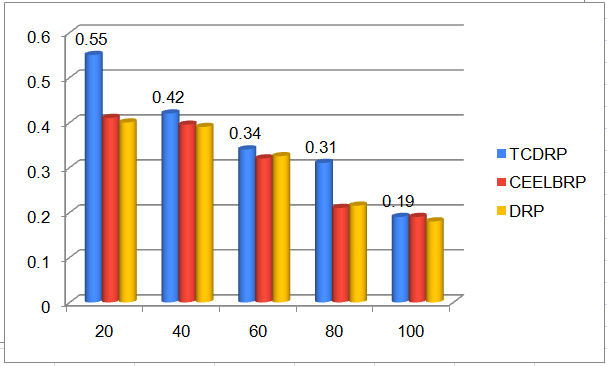
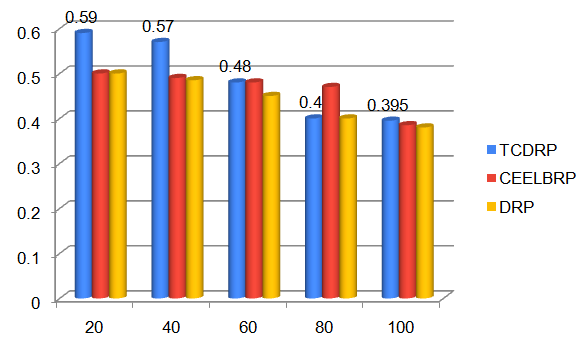
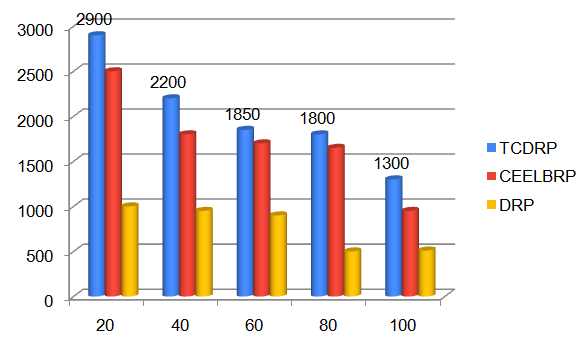
The TCDRP approach improves performance by using a modified TSA to determine the best path and a Cross layer enabled and ND-aware TCDMAC protocol to transmit data. The packet delivery ratio for TCDRP, CEELBRP, and DRP in relation to non-linear topology with node addition is shown in Figure 3. Comparative Summary of Nodes Vs. delivery ratio when nodes are added to the system in Figure 4. The delivery ratio in all three protocols drops linearly. The TCDMAC technique, which operates at the medium access layer beneath TCDRP, makes use of the ND information that is accessible across the network stack to provide flexibility in the route initiation procedure. The medium access mechanism also modifies frame length to accomplish adaptation (a collection of bits is bundled into frames of varying length with respect to ND). To attain a comparatively higher packet delivery ratio, adaptive DMP is utilized in conjunction with directional beam data transmission. As a result, in terms of delivery ratio, the TCDRP performs better than the DRP and has slight advantages over the CEELBRP.
The throughput achieved in the TCDRP, CEELBRP, and DRP for the non-linear topology when numbers of nodes in the simulations are changed is displayed in Figures 5 and 6. As the number of nodes in the system increases, all three protocols exhibit a trend towards decreased throughput. The TCDR’s average throughput is 21% higher than the CEELBRP’s and 48% higher than the DRP’s.
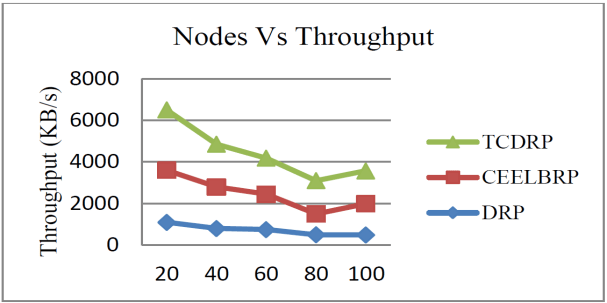
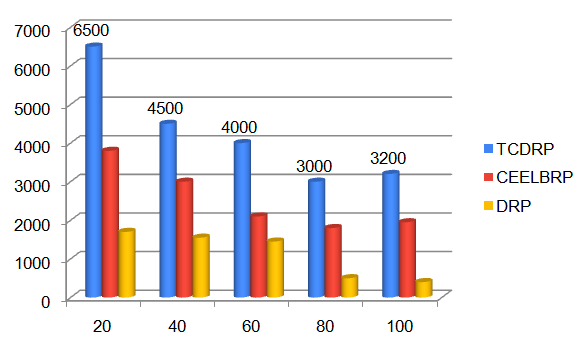
4.3. Based on Traffic Rates
The performance of suggested method is checked at various traffic rates, traffic flow is set as 50, 100, 150, 200 and 250 Kbps for allotted 100 nodes in the non-linear topology.
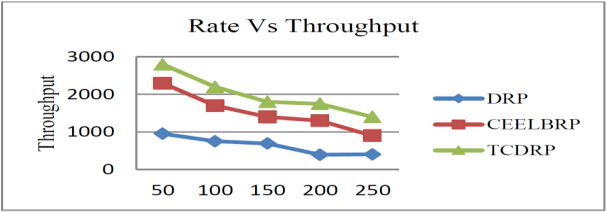
The delivery ratio of packets in the TCDRP, CEELBRP, and DRP for the non-linear topology where the traffic rate is altered is as shown in Figures 7 and 8. Delivery ratios for all tested protocols show a linear decline with increasing traffic rates. The TCDRP’s average delivery ratio value is 12% higher than the CEELBRP’s and 18% higher than the DRP’s.
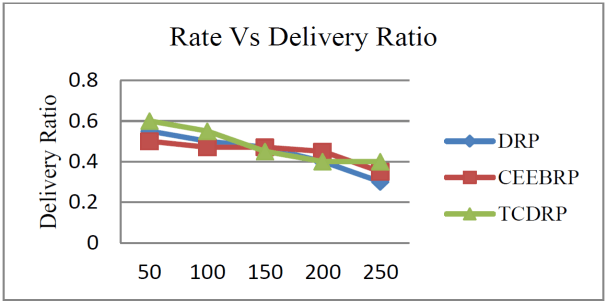
The throughput of the TCDRP, CEELBRP, and DRP for different traffic rates is displayed in Figures 9 and 10. In order to increase throughput, the TCDRP’s joint optimization of traffic in route establishment relies on minimum loss of routes rather than longer hops. The TCDRP has a throughput that is 25% higher than the CEELBRP and 44% higher than the DRP.
5. Conclusion
The MANET conundrum, in which ineffective path identification leads to a shorter network lifetime, is partially resolved by the development of diverse routing forms in recent years. In this study, the routing path is optimized using the bio-inspired modified tunicate swarm method. NS2 is used to simulate TCRDP, which is then examined in a range of scenarios and evaluated for packet delivery success and throughput metrics. The experimental results of the TCRDP technique demonstrate that a notably different approach to CLI in MANETs enables more precise adjustments to the state of the network. The evaluation results demonstrate that the suggested configuration performed better than both the most basic and routing protocols.
6. Future works
This research project entails the analysis of basic performance matrices and the development of a basic structure based on TSA and CLI concepts. Other performance metrics, such as protocol overhead and energy consumption, will be calculated and analyzed in subsequent work.
- Zheng, C. Li, P. H. J. Chong, et al., “MONET Special Issue on Towards Future Ad Hoc Networks: Technologies and Applications (II),” Mobile Networks and Applications, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 453–456, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11036-021-01731-7.
- Liu, et al., “Trajectory prediction training scheme in vehicular ad‑hoc networks based on federated learning,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 178, 2025, Art. no. 103917, doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2025.103917.
- Hong, M. Gerla, G. Pei, and C.-C. Chiang, “A group mobility model for ad hoc wireless networks,” in Proc. 2nd ACM Int. Workshop on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems (MSWiM), 1999, pp. 53–60, doi: 10.1145/313237.313248.
- C. Eberhart and J. Kennedy, “A new optimizer using particle swarm theory,” in Proc. 6th Int. Symp. Micro Machine and Human Science (MHS), Nagoya, Japan, 1995, pp. 39–43, doi: 10.1109/MHS.1995.494215.
- Dorigo, G. Di Caro, and L. M. Gambardella, “AntNet: Distributed stigmergetic control for communications networks,” Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, vol. 9, pp. 317–365, 1998, doi: 10.1613/jair.530.
- R. Jabbarpour, R. Ibrahim, S. Shamshirband, and M. Zarebavani, “Ant colony optimization for vehicle traffic systems: applications and challenges,” International Journal of Bio‑Inspired Computing, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 32–56, 2014, doi: 10.1504/IJBIC.2014.059970.
- Di Caro, F. Ducatelle, and L. M. Gambardella, “AntHocNet: an ant‑based hybrid routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks,” in Parallel Problem Solving from Nature—PPSN VIII, LNCS 3242, Springer, 2004, pp. 461–470, doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30217-9_47.
- Ducatelle, G. Di Caro, and L. M. Gambardella, “Ant agents for hybrid multipath routing in mobile ad hoc networks,” in Proc. 2nd Annu. Conf. Wireless On‑Demand Network Systems and Services (WONS), St. Moritz, Switzerland, 2005, pp. 44–53, doi: 10.1109/WONS.2005.3.
- Yuan, ACO‑based routing algorithms for wireless mesh networks, Master’s thesis, Concordia Univ., Montréal, QC, Canada, 2009.
- Marwaha, C.-K. Tham, and D. Srinivasan, “A novel routing protocol using mobile agents and reactive route discovery for ad hoc wireless networks,” in Proc. 10th IEEE Int. Conf. on Networks (ICON), Singapore, Aug. 2002, pp. 311–316.
- Liu, M. Z. Kwiatkowska, and C. Constantinou, “A biologically inspired QoS routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks,” in Proc. 19th Int. Conf. Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), 2005, pp. 426–431, doi: 10.1109/AINA.2005.13.
- Liu, M. Z. Kwiatkowska, and C. Constantinou, “A biologically inspired QoS routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks,” International Journal of Wireless and Mobile Computing, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 64–75, 2010, doi: 10.1504/IJWMC.2010.033054.
- Liu, M. Z. Kwiatkowska, and C. Constantinou, “A swarm intelligence routing algorithm for MANETs,” in Proc. 3rd IASTED Int. Conf. Communications, Internet and Information Technology (CIIT), St. Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, Nov. 2004, pp. 484–489.
- F. Wedde, M. Farooq, T. Pannenbaecker, B. Vogel, C. Mueller, J. Meth, and R. Jeruschkat, “BeeAdHoc: an energy efficient routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc networks inspired by bee behavior,” in Proc. 7th Annu. Conf. Genetic and Evolutionary Computation (GECCO), 2005, pp. 153–160.
- Chaudhary, “Bee‑inspired routing protocols for mobile ad hoc network (MANET),” Journal of Emerging Technologies in Web Intelligence, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 86–88, 2010.
- Seetaram and P. S. Kumar, “Energy‑aware ad hoc on‑demand multipath distance vector protocol for QoS routing,” World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology – International Journal of Computer, Electrical, Automation, Control and Information Engineering, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 826–830, 2015.
- -Y. Wu and H.-T. Song, “Ant‑based energy‑aware disjoint multipath routing algorithm for MANETs,” The Computer Journal, vol. 53, no. 2, pp. 166–176, 2010, doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxn007.
- Jamali, L. Rezaei, and S. J. Gudakahriz, “An energy‑efficient routing protocol for MANETs: a particle swarm optimization approach,” Journal of Applied Research and Technology, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 803–812, 2013, doi: 10.1016/S1665‑6423(13)71586‑4.
- H. Wolpert and W. G. Macready, “No‑Free‑Lunch Theorems for Optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 67–82, 1997, doi: 10.1109/4235.585893.
- M. Rizk‑Allah, O. Saleh, E. A. Hagag, et al., “Enhanced Tunicate Swarm Algorithm for Solving Large‑Scale Nonlinear Optimization Problems,” International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, vol. 14, 2021, Art. no. 189.
- Miyaji, M. Kawai, H. Uehara, and T. Ohira, “Directional Monitoring MAC Protocol Using Smart Antennas in Wireless Multi‑hop Networks,” in Proc. 2nd IEEE Int. Conf. on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), 2010, doi: 10.1109/ICUFN.2010.5547208.
- Toumpis, “Mother nature knows best: A survey of recent results on wireless networks based on analogies with physics,” Computer Networks, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 360–383, 2008, doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2007.08.011.
- Bulusu, D. Estrin, L. Girod, J. Heidemann, and USC/ISI, “Scalable Coordination for Wireless Sensor Networks: Self‑Configuring Localization Systems,” in Proc. 6th Int. Symp. on Communication Theory and Applications (ISCTA ’01), 2001, pp. 1–6.
- “The Network Simulator (ns‑2),” [Online]. Accessed: Sep. 7, 2025. http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/
- Latiff, N. Fisal, S. A. Arifin, and A. A. Ahmed, “Directional routing protocol in wireless mobile ad hoc network (MANETs),” in Trends in Telecommunications Technologies, C. J. Bouras, Ed. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech, 2010.
- A. Alghamdi, “Cuckoo Energy‑Efficient Load‑Balancing On‑Demand Multipath Routing Protocol,” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, vol. 47, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s13369-021-05841-y.
- Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar, Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi, “Harnessing the Power of Machine Learning and Sensor Detection in a Simulation for the Design of Smart Date Harvesting Robot”, Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1–8, 2026. doi: 10.55708/js0502001
- Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar, Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi, “Model Uncertainty Quantification: A Post Hoc Calibration Approach for Heart Disease Prediction “, Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 4, no. 12, pp. 25–54, 2025. doi: 10.55708/js0412003
- Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar, Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi, “Comparative Analysis of Supervised Machine Learning Models for PCOS Prediction Using Clinical Data”, Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 16–26, 2025. doi: 10.55708/js0406003
- Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar, Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi, “Fire Type Classification in the USA Using Supervised Machine Learning Techniques”, Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 4, no. 6, pp. 1–8, 2025. doi: 10.55708/js0406001
- Sadanand Ramchandrarao Inamdar, Jayashree Irappa Kallibaddi, “AI-Driven Digital Transformation: Challenges and Opportunities”, Journal of Engineering Research and Sciences, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 8–19, 2025. doi: 10.55708/js0404002

